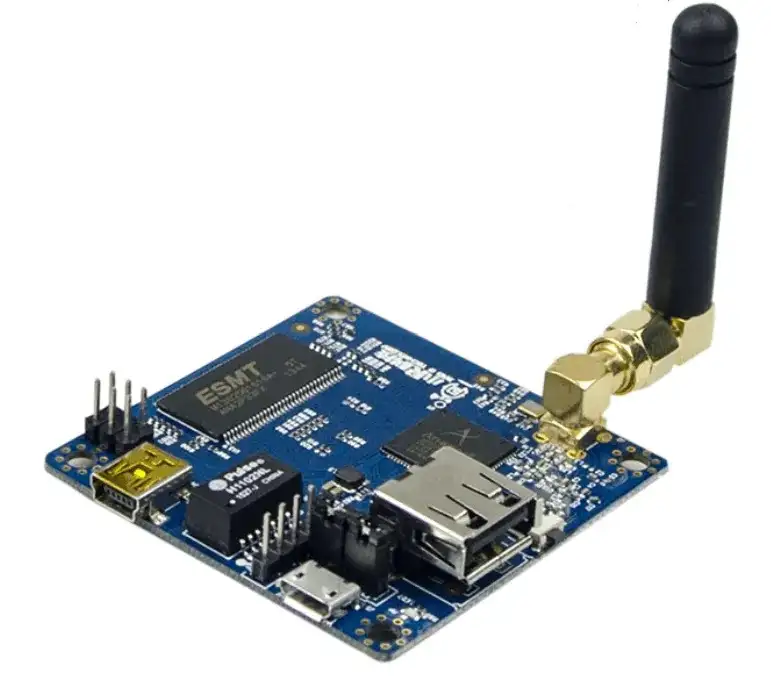


Expert RF PCB Manufacturer You Can Rely On
Why HUANG TE PCB for RF PCBs?
Experience
30+ Years of Manufacturing Experience
Specialized
Specialized in High-Frequency & Microwave PCBs
Certified
Certified with ISO, UL, and RoHS Standards
Equipment
Advanced Equipment for Precision Fabrication
Delivery
Quick Turnaround & Global Delivery
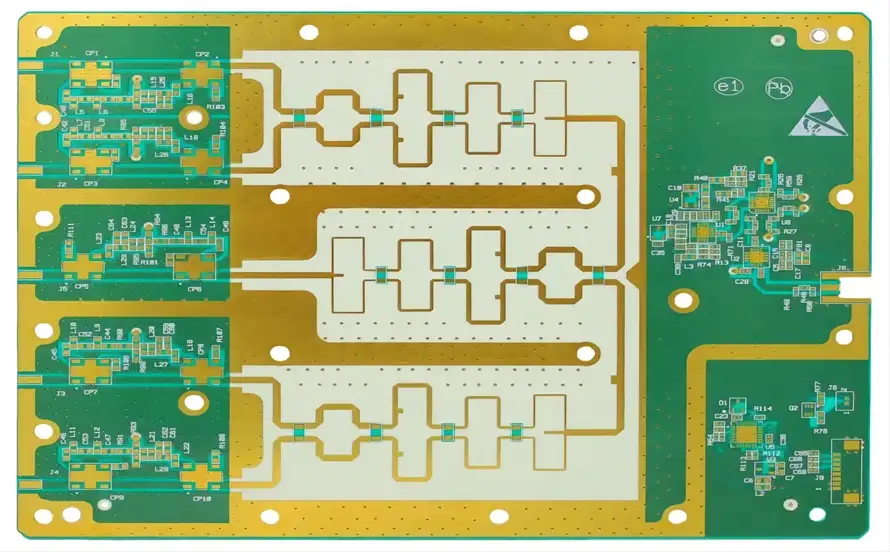
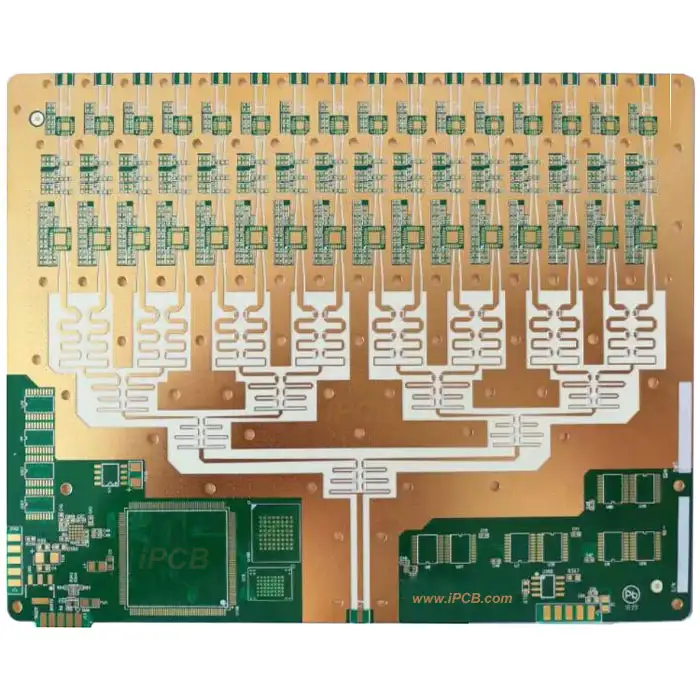
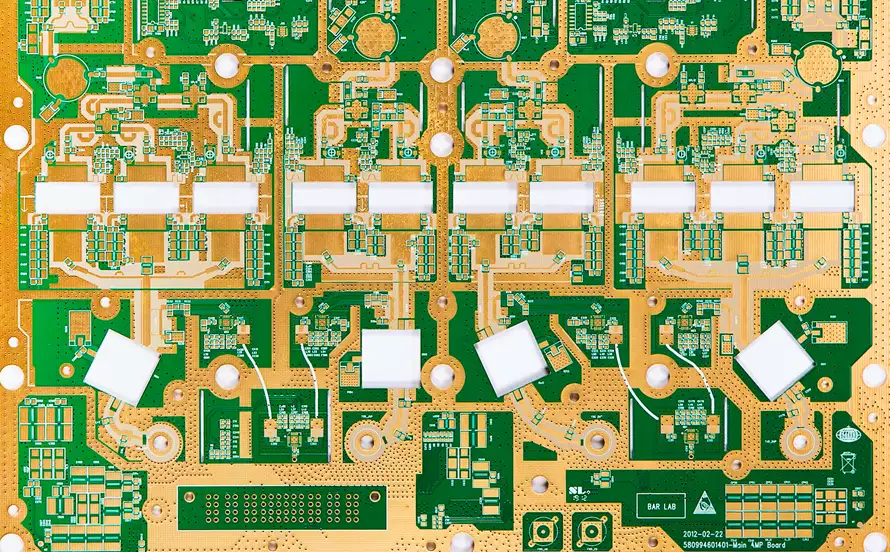
RF PCB Capabilities You Can Trust
- Frequency range: Up to 77 GHz
- Layers: 2 to 20
- Minimum trace/space: 4 mil
- Dielectric tolerance control
- Controlled impedance and stackup simulation
- Hybrid and PTFE-based materials available
- Surface finishes: ENIG, Immersion Silver, Hard Gold
Materials We Work With
| Material | Dk | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| RO4003C | 3.38 | Cost-effective, processable like FR4 | Antennas, RF circuits, automotive radar |
| RO4350B | 3.48 | Low loss, stable over frequency and temperature | Power amplifiers, base stations, GPS |
| RO3003 | 3.00 | Ultra-low loss, stable electrical properties | Microwave circuits, radar, aerospace |
| RO3010 | 10.2 | High Dk, excellent dimensional stability | Compact RF devices, filters |
| RT/duroid 5880 | 2.20 | Very low dielectric loss, high-frequency stability | High-frequency aerospace and satellite systems |
| RT/duroid 6002 | 2.94 | Low loss tangent, low CTE | Precision antennas, military applications |
| RO3203 / RO3206 / RO3210 | 3.02–10.2 | Thermoset resin, higher thermal conductivity | RF power amplifiers, filters |
| Material | Dk | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| IS620 | 3.2–3.4 | Stable electrical and thermal performance | Communication devices |
| I-Tera MT40 | 3.45 | Very low loss, lead-free compatible | Data centers, RF backplanes |
| Astra MT77 | 3.00 | Excellent for mmWave and 5G frequencies | 5G antennas, radar sensors |
| IS680 / IS680-345 | 3.38 | Designed for RF/microwave and hybrid applications | Wireless infrastructure |
| Material | Dk | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Megtron 4 / 6 / 7 | 3.4–3.6 | Extremely low loss, ideal for high-speed digital signals | Routers, servers, 5G networking |
| Megtron GX | ~3.2 | Designed for ultra-low loss, data-intensive boards | High-speed transmission, HPC |
| R-5515 / R-5410 | 2.9–3.2 | Stable in harsh environments | Automotive radar |
| Material | Dk | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| TLY-5 / TLY-5A | 2.2–2.33 | Ultra-low Dk, very low loss tangent | Antennas, microwave communications |
| RF-35 | 3.5 | Stable electrical properties, easy to process | RF/microwave, LNBs |
| TLX series | 2.45–2.65 | Balanced performance and cost | Commercial RF boards |
| CER-10 | 10.2 | High dielectric constant | Compact antennas, filters |
| Rogers/Taconic HYBRIDS | Varies | Combines Taconic high-frequency layer + FR4 | Cost-sensitive RF boards |
| Material | Dk | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AD255C / AD450 | 2.55–4.5 | Low PIM, low moisture absorption | Antennas, filters |
| CLTE / CuClad series | 2.2–2.9 | Ceramic-filled PTFE, ultra-stable | Aerospace, satellite |
| IsoClad 917 / 933 | ~2.3 | Low-loss PTFE-based materials | Low-frequency radar |
| Material | Dk | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| VT-47 / VT-464 | 4.3–4.6 | Mid-loss material, lead-free compatible | RF digital hybrid boards |
| VT-901 / VT-47H | ~3.8 | Excellent signal integrity | IoT, telecom |
| VT-441 / VT-825 | 3.5–3.8 | Low loss, available globally | Industrial RF modules |
| Material | Dk | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| S7439 / S1000H | 3.7–4.2 | FR4-based with better high-frequency response | WiFi modules, RF boards |
| SPE100 / SPE200 | ~3.0 | Competitive pricing, improved loss | Entry-level RF products |
| Brand | Material / Series | Dk Range | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doosan | DS-7409D / DS-8909F | 3.2–4.0 | Improved loss factor over FR4 |
| TUC (Taiwan Union) | TU-872LK / TU-883 | 3.0–3.6 | Low Df, used in high-speed applications |
| Nelco | N4000 series | ~3.7 | High-speed, aerospace compatible |
| Park/Nelco | M-Ply / M-Preg | 3.4–3.6 | Hybrid PCB materials |









Applications of Our RF PCBs
Applications
HUANG TE Group provide products and services in Automotive and Electric vehicl, Medical, Aviation, , etc.
- 5G Base Stations
- Radar & Satellite Systems
- Automotive Radar (ADAS)
- Aerospace & Military
- Wireless Modules (Wi-Fi, GPS, NB-IoT)
- Medical Imaging Devices
services
The difference between high frequency PCB and ordinary board
High-frequency and high-speed PCB boards, as printed circuit boards with frequencies exceeding 1GHz, may have different definitions in the industry. However, this type of board is known for its excellent physical properties, high precision and strict technical parameter requirements, and is widely used in cutting-edge fields such as communication systems, automotive ADAS systems, satellite communications and radio systems.
In addition to RF systems, modern devices also cover digital processing and interface parts. Driven by consumer demand for faster Internet connections, mobile HD video and the Internet of Things, PCB boards must not only meet high-frequency performance, but also support high-speed digital data transmission. Commercial applications such as IoT, 5G, and big data centers, as well as an increasing number of personal applications, are constantly refreshing the speed requirements of digital communication systems. According to statistics, driven by data rates, the bandwidth of high-speed digital systems doubles almost every three years.
Although the production process of high-frequency and high-speed PCB boards is similar to that of ordinary PCB boards, the core difference lies in the properties of their raw materials. The main material used in high-frequency and high-speed PCB boards is high-frequency and high-speed copper clad laminate, which has a low dielectric constant (Dk) and a low dielectric loss factor (Df). These two parameters are crucial to ensure the speed and quality of signal transmission.
| Type | High Frequency PCB | Ordinary PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric constant (Dk) | High-frequency and high-speed PCB boards require the dielectric constant of the substrate to be small and stable, because the signal transmission rate is inversely proportional to the square root of the material dielectric constant. High dielectric constants can easily cause signal transmission delays. | In contrast, ordinary PCB boards have relatively low requirements for dielectric constants and focus more on meeting general circuit connection needs. |
| Dielectric loss factor (Df) | High-frequency and high-speed PCB boards require that the dielectric loss of the substrate must be small to reduce attenuation and heat generation during signal transmission. | Ordinary PCB boards have relatively low requirements in this regard. |
| Impedance characteristics | One of the basic principles of high-speed design is impedance control, and high-frequency and high-speed PCB boards have strict requirements for this to ensure the stability and integrity of signal transmission. | Ordinary PCB boards usually have looser requirements for impedance control. |
| Water absorption | High-frequency and high-speed PCB boards require low water absorption of the substrate to prevent changes in dielectric constant and dielectric loss when wet. | Ordinary PCB boards usually have lower requirements in this regard. |
