Aluminum Core PCB
- What is Aluminum Core PCB(Aluminum Substrate PCB)?
- Structure of Aluminum Core PCB
- The advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum PCB
- Performance of Aluminum PCBs
- Challenges of Aluminum Core PCBs Manufacturing
Aluminum Core PCBs feature a metal-based structure designed to overcome the thermal limitations of traditional FR4 boards. By replacing the fiberglass substrate with an aluminum base, these boards effectively dissipate heat generated by high-power components.
Aluminum PCBs are the industry standard for applications where thermal management is critical.
They are extensively used in LED lighting and power conversion electronics, where high-intensity components generate substantial heat. By utilizing a metal substrate, these boards provide a low-thermal-resistance path to rapidly transfer heat away from sensitive components. This efficient cooling prevents thermal failure, significantly extending the lifespan of LED devices and ensuring long-term operational stability.
Typically, aluminum PCBs are single-sided, although they can also be manufactured as double-sided boards. While multilayer aluminum PCBs exist, they are notably more complex and challenging to produce.
The standard design of an aluminum PCB features one side that is white, intended for soldering LED pins, while the opposite side showcases the natural aluminum color, often treated with a thermally conductive paste to facilitate heat transfer. This design is particularly advantageous in various industries, including street lighting, stop lights, and household lighting, where efficient heat management is essential.
In summary, aluminum PCBs are a vital component in modern electronics, especially where heat dissipation is a priority, enabling enhanced performance and longevity in various applications.
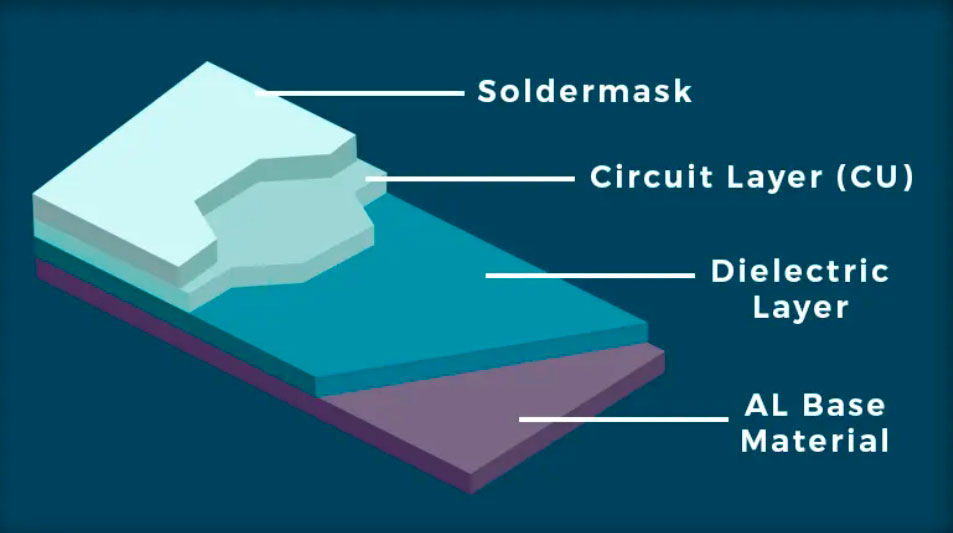
The aluminum substrate is a typical metal substrate, so its structure is the same as the metal substrate.
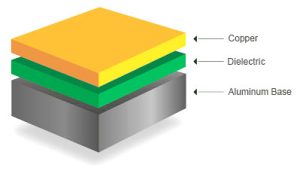 | 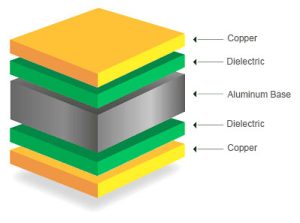 | 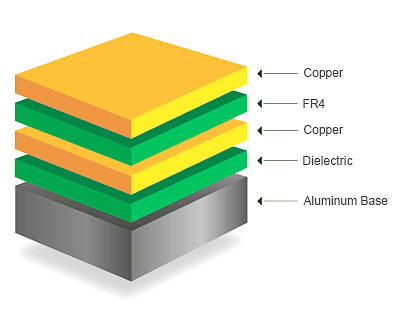 | 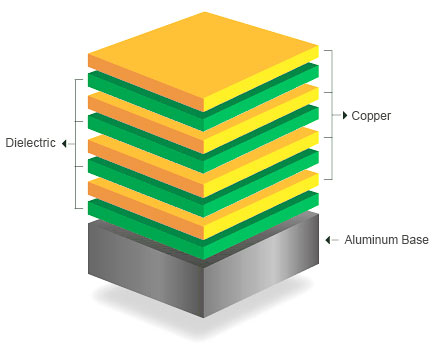 |
Advantages:
Excellent Heat Dissipation: Aluminum PCBs are highly effective at transferring heat away from sensitive components, which minimizes the risk of damage in high-temperature applications.
Enhanced Durability: Aluminum offers superior strength compared to ceramic or fiberglass substrates, reducing the likelihood of breakage during manufacturing and usage.
Environmental Friendliness: Aluminum is recyclable and non-toxic, aligning with sustainability goals and energy conservation during assembly.
Lightweight: Despite their durability, aluminum PCBs are lightweight, making them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace and mobile devices.
Disadvantages:
Higher Cost: The manufacturing process for aluminum PCBs can be more complex and costly compared to standard fiberglass-based PCBs.
Process Complexity: Working with aluminum requires specialized techniques for welding and routing, increasing production difficulties.
Limited Applications: Aluminum PCBs are best suited for high-power devices with significant heat dissipation needs, making them less ideal for low-power applications.
Potential Susceptibility: Aluminum can be vulnerable to corrosion from certain environmental factors, particularly halide ions like chloride.
In summary, while aluminum PCBs offer significant advantages in heat management, durability, and environmental impact, their higher costs and specialized manufacturing processes can limit their use to specific applications.
1. Thermal Dissipation
Aluminum PCBs excel in thermal management, addressing a significant limitation of common PCB substrates like FR4 and CEM3, which are poor thermal conductors. Efficient heat dissipation is crucial; without it, electronic components can experience high-temperature failures. Aluminum substrates facilitate superior thermal dissipation, ensuring that heat generated by electronic devices is effectively distributed, thereby enhancing overall performance and reliability.
2. Thermal Expansion
The aluminum substrate effectively mitigates issues related to thermal expansion and contraction of components. As temperatures fluctuate, components made from different materials can expand or contract at varying rates, potentially leading to mechanical stress and failure. Aluminum substrates alleviate these concerns, particularly in SMT (Surface Mount Technology) applications, improving the durability and reliability of the entire electronic assembly.
3. Dimensional Stability
Aluminum PCBs demonstrate excellent dimensional stability compared to insulating materials. When subjected to temperature changes—from 30 °C to 140-150 °C—aluminum substrates experience only a minimal dimensional change of about 2.5-3.0%. This stability is crucial for maintaining the integrity and functionality of electronic circuits under varying thermal conditions.
4. Other Performance Attributes
In addition to thermal advantages, aluminum substrates provide shielding effects and can serve as a robust alternative to brittle ceramic substrates. They enhance heat resistance and physical properties, which contribute to the overall performance of the circuit board. Furthermore, the use of aluminum substrates can lead to reduced production costs and labor, making them a cost-effective choice in various applications.
Applications of Aluminum PCBs
Aluminum PCBs are renowned for their excellent thermal dissipation capabilities, making them ideal for various applications, particularly in environments where heat management is critical. Here are some of the key applications of aluminum PCBs across different industries:
LED Lighting
Due to the significant heat generated by LEDs, aluminum substrates are commonly used in LED circuit boards. They ensure efficient heat dissipation, extending the lifespan and performance of LED lamps.
Audio Equipment
Aluminum PCBs are utilized in a range of audio devices, including input/output amplifiers, balanced amplifiers, audio amplifiers, preamplifiers, and power amplifiers. Their thermal management properties help maintain sound quality and device reliability.
Power Supply Devices
In power supply applications, aluminum PCBs are used in stabilizers, conditioners, and DC-AC adapters. Their durability and heat resistance are critical for maintaining performance in high-power situations.
Communication Electronics
High-frequency amplifiers, filtering circuits, and transceiver circuits benefit from the thermal stability provided by aluminum PCBs, ensuring reliable operation in communication devices.
Office Automation Equipment
In devices such as motor drivers and automated office equipment, aluminum PCBs contribute to efficient operation and reliability, particularly under varying thermal conditions.
Computers
Aluminum substrates are found in power supply devices, floppy disk drives, motherboards, and other computer components where heat dissipation is essential for performance and longevity.
Power Modules
Applications such as inverters, solid-state relays, and rectifier bridges utilize aluminum PCBs to manage heat effectively and enhance reliability in power conversion processes.
Industrial Vehicles
In automotive applications, aluminum PCBs are employed in ignition systems, voltage regulators, and automatic safety control systems, where durability and thermal management are vital.
Switches and Microwave Devices
Aluminum PCBs are also used in radiators, semiconductor devices, thermal insulation, and motor controllers, providing efficient thermal performance.
LED Displays
In both standalone LED displays and displays that utilize LED light sources, aluminum substrates are critical for managing heat, ensuring effective operation and visual performance.
The production of aluminum PCBs presents several significant challenges that require careful management to ensure optimal performance and quality. Here are some of the primary challenges encountered during the manufacturing process:
1.Mechanical Processing
Drilling aluminum substrates must be performed without leaving burrs on the edges of holes, as these can affect pressure testing results. The milling process can be particularly challenging, and precise shaping often requires advanced molds. Ensuring that edges are neat and undamaged, especially around solder masks, is critical. Techniques like up-cut and down-pull punching necessitate skilled handling to maintain board curvature within 0.5%.
2.Avoiding Surface Scratches
Aluminum surfaces are prone to discoloration and damage from contact or exposure to certain chemicals. Maintaining the integrity of the aluminum finish throughout the manufacturing process is crucial; even minor scratches can lead to customer rejection. Companies often employ passivation processes or protective films to mitigate these risks.
3.High Voltage Testing
For communication power aluminum substrates, 100% high voltage testing is mandatory, with specifications often requiring either DC or AC voltage of 1500V to 1600V for durations of 5 to 10 seconds. Contaminants, burrs, or damage to insulation can lead to failure during testing, resulting in rejections for boards that show delamination or bubbling.
4.Thick Copper Etching
Aluminum PCBs used in high-power applications often feature thicker copper foils (3oz or higher). Etching such thickness requires careful compensation for trace width to maintain tolerance levels. Precise design and control of etching parameters are essential to ensure trace integrity and meet impedance specifications.
5.Solder Mask Printing
The presence of thick copper foils complicates solder mask printing due to differences in surface levels between traces and substrates. Successful adhesion of the solder mask may require the use of high-quality materials and possibly double printing. In some cases, resin filling prior to solder mask application may be necessary.
6.Mechanical Manufacturing
Mechanical processes like drilling, milling, and V-cutting are critical in aluminum PCB production. Burrs left in internal vias during drilling can compromise electrical strength. To maintain high-quality results, especially in small batch productions, the use of specialized milling tools and careful adjustment of drill parameters is essential.
